What Are the Costs of Using Amazon Web Services (AWS)?
Amazon Web Services (AWS) offers various services, including computing power, storage options, and databases, each with distinct pricing structures. These costs can be unpredictable without proper management due to factors like on-demand usage, types of compute instances, data transfer, storage needs, and service configuration variances.
Understanding AWS cost can help organizations budget for cloud expenses and only pay for necessary services. Organizations must navigate AWS’s pricing model to get the most value for their money. This involves analyzing usage patterns and making informed decisions on resource allocation.
Understanding AWS Pricing Models
Pay-as-You-Go
The pay-as-you-go model allows users to pay only for the resources they consume without upfront commitments. Charges are based on usage and stop when resources are no longer used, providing flexibility and scalability. This model is suitable for users with changing workloads or short-term projects that require rapid scaling. It encourages cost-efficiency by aligning spending directly with business activity and demand.
While providing flexibility, this model is typically the most expensive and can lead to unpredictable expenses if usage isn’t monitored closely. Organizations must establish usage monitoring to ensure the costs align with their budget. Additionally, evaluating usage patterns can reveal areas for potential optimization.
Reserved Instances and Savings Plans
Reserved instances (RIs) and savings plans offer significant cost savings for predictable workloads. Reserved instances allow users to reserve computing capacity for a one- or three-year term, while savings plans offer flexible pricing over a specified term for consistent usage patterns. Both models benefit organizations with steady and predictable application demands, allowing for substantial discounts compared to on-demand pricing.
These models require an upfront commitment but provide up to 72% savings. Organizations can maximize benefits by analyzing their application needs and choosing the appropriate plan. Efficient use of reserved instances and savings plans involves regularly reviewing and adjusting pledged capacity against actual usage trends.
Spot Instances
Spot instances offer unused AWS capacity at up to 90% off the on-demand price, allowing users to bid on spare resources. Ideal for flexible workloads or non-critical operations that can handle interruptions, spot instances provide significant cost savings for applications like big data, containerized workloads, and CI/CD testing. Organizations with adaptable workloads can significantly reduce computing costs by strategically utilizing spot instances.
However, spot prices vary based on demand, and resources can be reclaimed with only two minutes’ notice. Amazon publishes historic spot prices, updated every 5 minutes. Effective management involves taking advantage of instance automation features and ensuring that workloads are fault-tolerant.
Dedicated Hosts
Dedicated hosts provide a server physically dedicated to a user’s workload, offering control over server configurations, licensing, and compliance requirements. This model works well for enterprises needing dedicated resources for regulatory compliance or existing software license reuse. Utilizing dedicated hosts can help organizations meet stringent compliance standards.
Despite higher costs, dedicated hosts deliver value through customizable server setups and improved control over workloads. However, organizations must carefully assess workload requirements and existing software assets to use this model efficiently.
Related content: Read our guide to AWS cost optimization tools
Key Components Affecting AWS Costs
Compute Services Pricing
AWS compute services pricing largely depends on the type of instances used, the duration of usage, and the configurations. Instances vary across specification categories—such as general purpose, compute-optimized, memory-optimized—each priced differently. Understanding these pricing tiers helps users choose appropriate compute resources, avoiding unnecessary cost by aligning needs with the right instance type.
AWS offers various purchasing options: on-demand, reserved instances, spot instances, and savings plans, each impacting cost structure significantly. Organizations should analyze their workload requirements and usage patterns to select the most cost-effective purchase option. Additionally, elasticity features like auto-scaling can further optimize AWS compute expenses.
Storage Services Pricing
Storage costs in AWS are influenced by the volume of data stored, data retrieval frequency, and chosen storage class. AWS offers multiple storage classes, including S3 Standard (for frequent access), S3 Infrequent Access (lower cost storage for less frequently accessed data), and Glacier (long-term archival), each tailored for different use cases based on access needs and price. Customers should select appropriate storage classes for efficient cost management according to data access patterns.
In addition to object storage, AWS provides Elastic Block Store (EBS), a high-performance block storage service designed for EC2 instances, offering persistent storage with varying performance levels based on volume type. AWS also offers Elastic File System (EFS), a scalable file storage service that supports multiple compute instances and is compatible with Linux-based operating systems. For Windows workloads, Amazon FSx provides managed file storage optimized for Windows File Server and Lustre.
Data Transfer Costs
Data transfer costs can significantly impact the overall AWS bill, particularly for applications with high data movement, such as content delivery, data analytics, and distributed applications. These costs occur when data moves between AWS regions, between AWS and the internet, or between services within a region. Organizations can optimize costs by using AWS PrivateLink, VPC peering, or content delivery networks (CDNs) like CloudFront to reduce unnecessary transfers and improve efficiency.
Organizations should evaluate their architecture to identify data transfer bottlenecks and optimize cost efficiency. Leveraging AWS services that offer free intra-region data transfer, such as private VPC connections or AWS PrivateLink, can reduce expenses. Planning data deployments to limit cross-region data movement can help control unwanted transfer costs.
Additional Service Charges
Additional service charges can arise from using AWS features and tools. These charges are often linked to features like elastic IPs, load balancers, automation services like AWS Lambda, or analytics services like AWS Athena. Organizations need to understand how the ancillary services they use contribute to the overall cost structure and identify where optimizations are possible.
Usage monitoring tools and detailed billing reports can help identify unexpected charges and their root causes. By pinpointing areas with excessive use of services, organizations can implement strategies to either reduce usage or switch to alternative solutions. Detailed cost analysis ensures organizations only pay for services that provide tangible benefits.

- Create layered cost optimization strategies: Implement a combination of cost strategies, such as using spot instances for non-critical workloads, reserved instances for predictable workloads, and auto-scaling for dynamic demands. This layered approach balances cost savings with operational resilience.
- Leverage Graviton instances for workloads: AWS Graviton-based instances, powered by Arm processors, often deliver better price-performance ratios than traditional x86-based instances. Test and migrate compatible workloads to Graviton for potential savings.
- Enable savings plans with granularity: Use Compute Savings Plans instead of EC2 Savings Plans if the workloads extend beyond EC2 instances, as Compute Plans include Fargate and Lambda, providing flexibility without compromising on savings.
- Analyze inter-region data transfer patterns: For applications deployed across multiple regions, minimize cross-region data transfer. Use regionally optimized architectures or AWS Global Accelerator to manage latency without unnecessary egress charges.
- Adopt proactive anomaly detection: Use AWS Cost Anomaly Detection to set up automated alerts for unexpected spikes in usage or cost, allowing admins to address inefficiencies or unauthorized usage before it escalates.
AWS Native Cost Management Tools
The AWS platform provides several built-in tools to help organizations monitor, plan and optimize their costs. However, these tools offer only basic functionality and present several challenges for organizations, causing many teams to adopt specialized cloud cost management tools.
AWS Cost Explorer
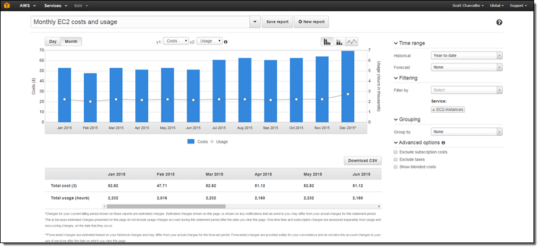
AWS Cost Explorer is a tool for managing AWS expenditures. It provides a detailed visualization of usage patterns and cost trends, enabling organizations to analyze cost drivers and forecast future expenses. Cost Explorer offers intuitive graphs and insights, allowing users to quickly identify key areas of spending and optimize their resource use.
Users can customize filters in Cost Explorer to focus on specific services, locations, or periods, enabling targeted analysis. Employing these features helps pinpoint inefficient resource allocations and reveals opportunities for spending reduction.
Challenges and limitations:
- Limited historical data retention (up to 12 months), restricting long-term trend analysis.
- Lacks real-time cost tracking, leading to potential delays in identifying cost spikes.
- Does not provide automated anomaly detection; users must manually monitor trends.
- Limited integration with third-party cost management tools for deeper financial insights.
AWS Budgets
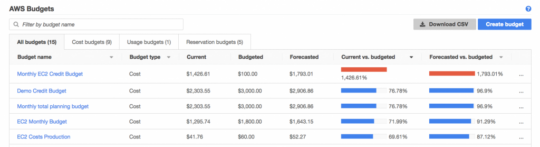
AWS Budgets enable users to set custom cost, usage, or reservation targets, sending alerts when thresholds are approached or exceeded. This proactive approach helps organizations stay within budget and ensures financial goals are not compromised. AWS Budgets offer a tailored experience, allowing for detailed tracking of expenses across projects or departments.
With AWS Budgets, users can set thresholds for total monthly spending, service-specific usage, or the consumption of resources tied to specific tags.
Challenges and limitations:
- Budget alerts only trigger after a threshold is exceeded, rather than in real-time.
- Requires manual configuration, which can be time-consuming for large organizations.
- Does not offer predictive analytics for future budget adjustments.
- Lacks deep insights into the root causes of budget overruns.
AWS Cost and Usage Report
The AWS Cost and Usage Report (CUR) comprehensively tracks all AWS usage and associated costs. CUR delivers granular data, breaking down expenditures by services, resource tags, and accounts, promoting detailed financial analysis. Utilizing CUR helps organizations understand the nuances of their AWS consumption and identify areas for cost reduction.
CUR enables automated data delivery to an S3 bucket, allowing for integration with business intelligence tools for deeper analysis. Through regular examination of CUR data, organizations gain insights into usage trends and potential inefficiencies, helping in strategic decision-making.
Challenges and limitations:
- Delivers raw, complex data that requires additional processing for meaningful insights.
- Report processing times can be delayed, limiting real-time cost monitoring.
- Requires external tools (e.g., AWS Athena, QuickSight) for analysis, adding complexity.
- Managing large datasets can be resource-intensive and expensive.
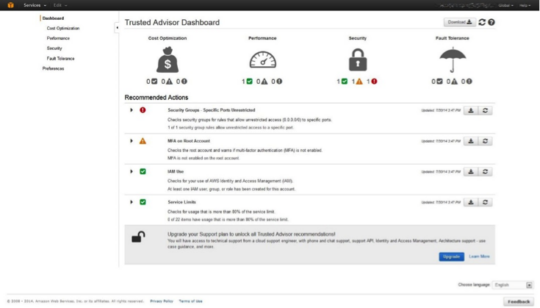
AWS Trusted Advisor
AWS Trusted Advisor recommends optimizing resources, security, and performance, consequently helping reduce costs. It evaluates AWS usage against best practices, identifying opportunities to save on spending. Trusted Advisor’s reports cover cost optimization, security, fault tolerance, and service limits, providing comprehensive insights into resource efficiency.
Organizations can leverage Trusted Advisor to pinpoint underutilized resources or identify areas where AWS pricing models like reserved instances might be more cost-effective.
Challenges and limitations:
- Advanced cost optimization checks are only available with Business or Enterprise Support plans.
- Limited recommendations for third-party integrations or external cost management strategies.
- Some cost-saving recommendations may not align with business-specific constraints.
- Does not provide real-time recommendations, requiring periodic manual reviews.
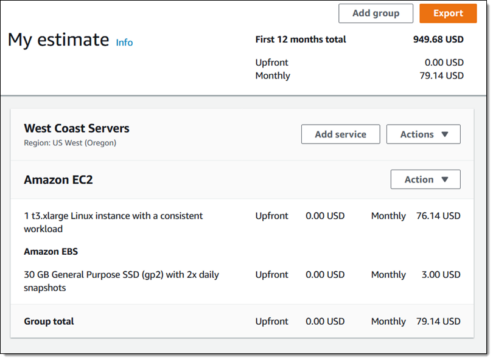
AWS Cost Calculator
The AWS Cost Calculator is a tool to estimate the cost of using AWS services based on anticipated workloads. It allows users to input details about their resource requirements, such as the number of instances, storage needs, and data transfer volumes, to generate an accurate cost forecast. This helps organizations plan their budgets effectively before committing to services.
The Cost Calculator supports a range of AWS services, enabling comparisons between different configurations. By adjusting parameters, users can evaluate the financial impact of scaling workloads or switching between pricing models like on-demand and reserved instances.
Challenges and limitations:
- Estimates may differ from actual costs due to fluctuating AWS pricing and discounts.
- Lacks support for complex pricing scenarios, such as multi-region deployments.
- Does not account for dynamic cost changes based on real-world usage fluctuations.
- Requires manual input of resource configurations, increasing the risk of errors.
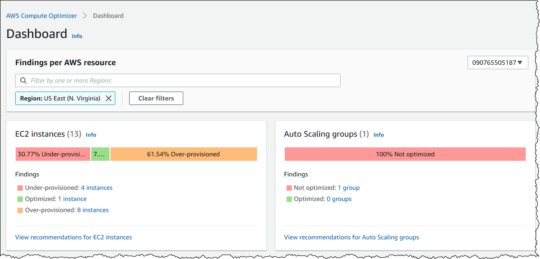
AWS Compute Optimizer
AWS Compute Optimizer helps improve cost efficiency and performance by analyzing usage patterns and providing recommendations for optimal compute resources. It evaluates instances, auto-scaling groups, and other compute services to identify over-provisioned or underutilized resources, suggesting adjustments to align with workload needs.
Compute Optimizer’s insights are driven by machine learning models that factor in historical usage data. For example, it can recommend smaller instance types or alternative configurations that deliver the same performance at lower costs. Additionally, it highlights opportunities to adopt cost-saving options like savings plans or spot instances.
Challenges and limitations:
- Only supports select AWS services, limiting its scope for a full cost optimization strategy.
- Recommendations are based on past usage data, which may not reflect future needs.
- Does not provide real-time recommendations for sudden workload changes.
- Requires manual implementation of optimization suggestions, increasing effort.
Learn more in our detailed guide to AWS cost management
7 Best Practices for AWS Cost Optimization
Here are some ways organizations can ensure they don’t overspend on AWS.
1. Right-Sizing Resources
Right-sizing resources involves adjusting instance types and configurations to match actual workload requirements. By regularly monitoring usage statistics, organizations can reduce expenses and improve performance by ensuring resource allocations are neither oversized nor underutilized.
Tools like AWS Compute Optimizer and Trusted Advisor aid right-sizing efforts, providing recommendations based on usage patterns. Managed efforts in right-sizing lead to significant cost savings by aligning infrastructure with business needs. Implementing regular reviews of resource utilization fosters an environment where financial resources are effectively utilized.
2. Utilizing Auto Scaling
Utilizing auto-scaling ensures AWS services adjust dynamically to changing demand, optimizing resource usage without manual intervention. This approach maintains application performance while minimizing costs by scaling resources up or down based on demand metrics. Auto-scaling helps prevent over-provisioning, delivering cost savings.
Effectively configuring auto-scaling policies requires an understanding of application demand patterns. Incorporating load testing and monitoring analytics can optimize these policies, ensuring they reflect real-world usage scenarios.
3. Leveraging Spot Instances
Leveraging spot instances offers substantial savings for flexible, fault-tolerant applications. Organizations can bid on unused AWS capacity, obtaining resources at a fraction of standard costs. Optimal for batch processing, big data jobs, and container workloads, spot instances reduce spend while maintaining performance for eligible tasks.
To benefit from spot instances, organizations must develop contingency strategies to handle sudden terminations inherent to spot instances. Automation tools enabling workload adaptation in response to resource availability are crucial.
4. Implementing Cost Allocation Tags
Implementing cost allocation tags is a straightforward practice to monitor and manage AWS expenses. Tags classify resources based on various metrics like department or project, providing visibility into cost centers. This granularity aids in more accurate budgeting and identifying where costs can be optimized.
Organizations can improve financial tracking and accountability by applying consistent tagging policies across all AWS resources. Tags enable detailed usage reports, enabling leaders to make informed decisions and optimize spending.
5. Regularly Reviewing Reserved Instances
Regularly reviewing reserved instances ensures that they align with current usage patterns and continue to offer cost advantages. This practice involves evaluating current reservations against actual usage, modifying, renewing, or selling them on secondary markets to avoid unnecessary costs. Reserved instances offer discounts compared to on-demand pricing but require ongoing management.
Organizations benefit by analyzing workloads to adjust reserved instance configurations for reflected demand changes. Allocating reserved capacity accurately avoids financial waste and maximizes savings. Through consistent oversight and adjustments, companies ensure they leverage RIs fully, optimizing AWS costs.
6. Optimizing Storage With Lifecycle Policies
Optimizing storage with lifecycle policies helps manage AWS costs by automatically transitioning data between different storage classes as it ages. Lifecycle policies allow organizations to move less-accessed data to lower-cost storage tiers like S3 Infrequent Access or Glacier, reducing expenses without compromising data availability.
Effective implementation of lifecycle policies involves analyzing data retrieval patterns and customizing policies to align with organizational needs. Regular policy reviews ensure storage management adapts to evolving data requirements. This proactive strategy uses AWS’s tiered storage to maintain cost-effectiveness as data volumes grow.
7. Continuous Cost Governance
Continuous cost governance involves regularly monitoring, analyzing, and managing AWS expenses to ensure ongoing financial efficiency. Establishing a governance framework requires policies, processes, and tools to evaluate expenditure, promoting strategic decision-making and cost accountability.
Developing a culture of continuous evaluation helps identify cost optimization opportunities. Aligning cloud financial management with business objectives maintains financial health and supports dynamic operational needs.
Learn more in our detailed guide to AWS cost optimization
AWS Cost Monitoring with Umbrella
Umberella is an AI-based cost management platform that adds an additional layer of insights of what AWS-native cloud optimization services offer.
Umbrella provides:
- Quick Integration: Connect your AWS Cost Monitoring data in minutes via the Data Manager section.
- Real-Time Monitoring: Automatically monitor all AWS Cost Monitoring data in real time to detect anomalous behavior.
- Anomaly Detection Alerts: Receive notifications of detected anomalies in your AWS Cost Monitoring data through various channels, including email, push notifications, Slack, PagerDuty, or Webhook.
- Forecasting: Run forecasts over your AWS Cost Monitoring data to plan effectively.
- Data Integration: Combine AWS Cost Monitoring metrics and events with other data sources into Umbrella’s centralized Autonomous Analytics platform for enhanced visibility across millions of metrics.